Java tutorial for Capstone
1. Basic sample
Capstone has a very simple API, so it is very easy to write tools using the framework. To start, the below code disassemble some X86 binary, and print out its assembly.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// Test.java
import capstone.Capstone;
public class Test {
public static byte [] CODE = { 0x55, 0x48, (byte) 0x8b, 0x05, (byte) 0xb8,
0x13, 0x00, 0x00 };
public static void main(String argv[]) {
Capstone cs = new Capstone(Capstone.CS_ARCH_X86, Capstone.CS_MODE_64);
Capstone.CsInsn[] allInsn = cs.disasm(CODE, 0x1000);
for (int i=0; i<allInsn.length; i++)
System.out.printf("0x%x:\t%s\t%s\n", allInsn[i].address,
allInsn[i].mnemonic, allInsn[i].opStr);
}
}
Readers can get the code from here. Output of this sample is like below:
$ javac Test.java
$ java -classpath /usr/share/java/jna/jna.jar:. Test
0x1000: push rbp
0x1001: mov rax, qword ptr [rip + 0x13b8]
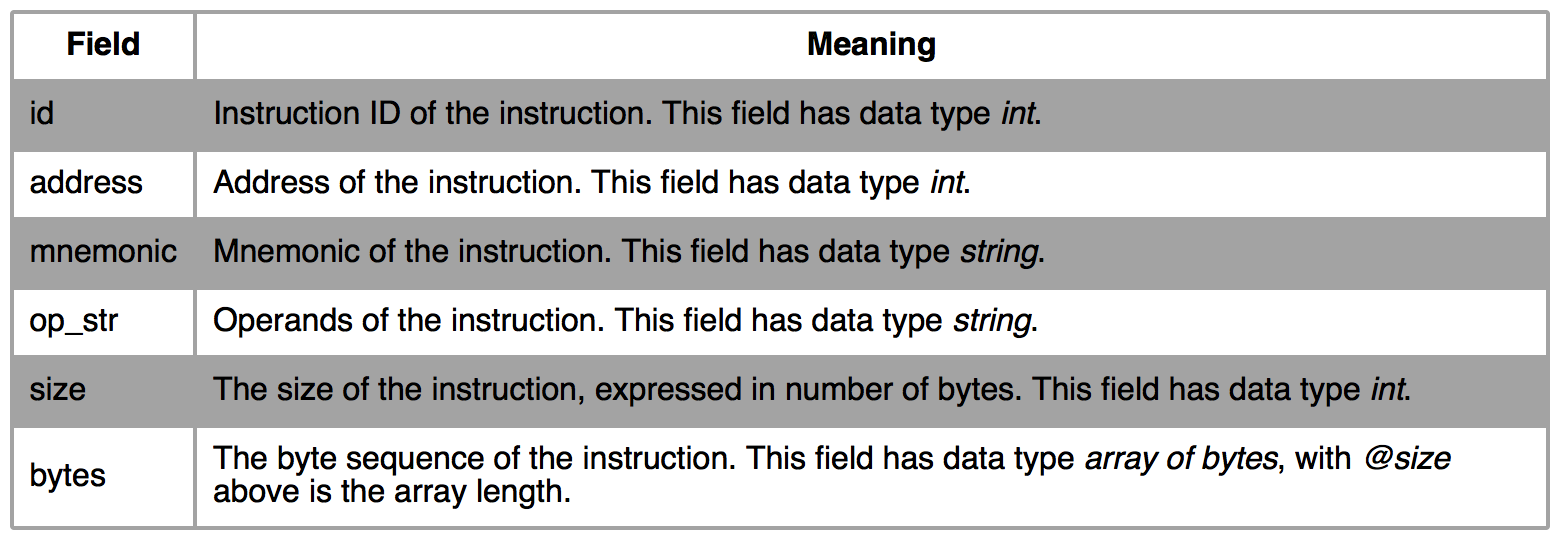
The structure CsInsn exposes all the internal information about the disassembled instruction we are looking at. Some of the most used fields of this structure are presented below.
2. Architectures and modes
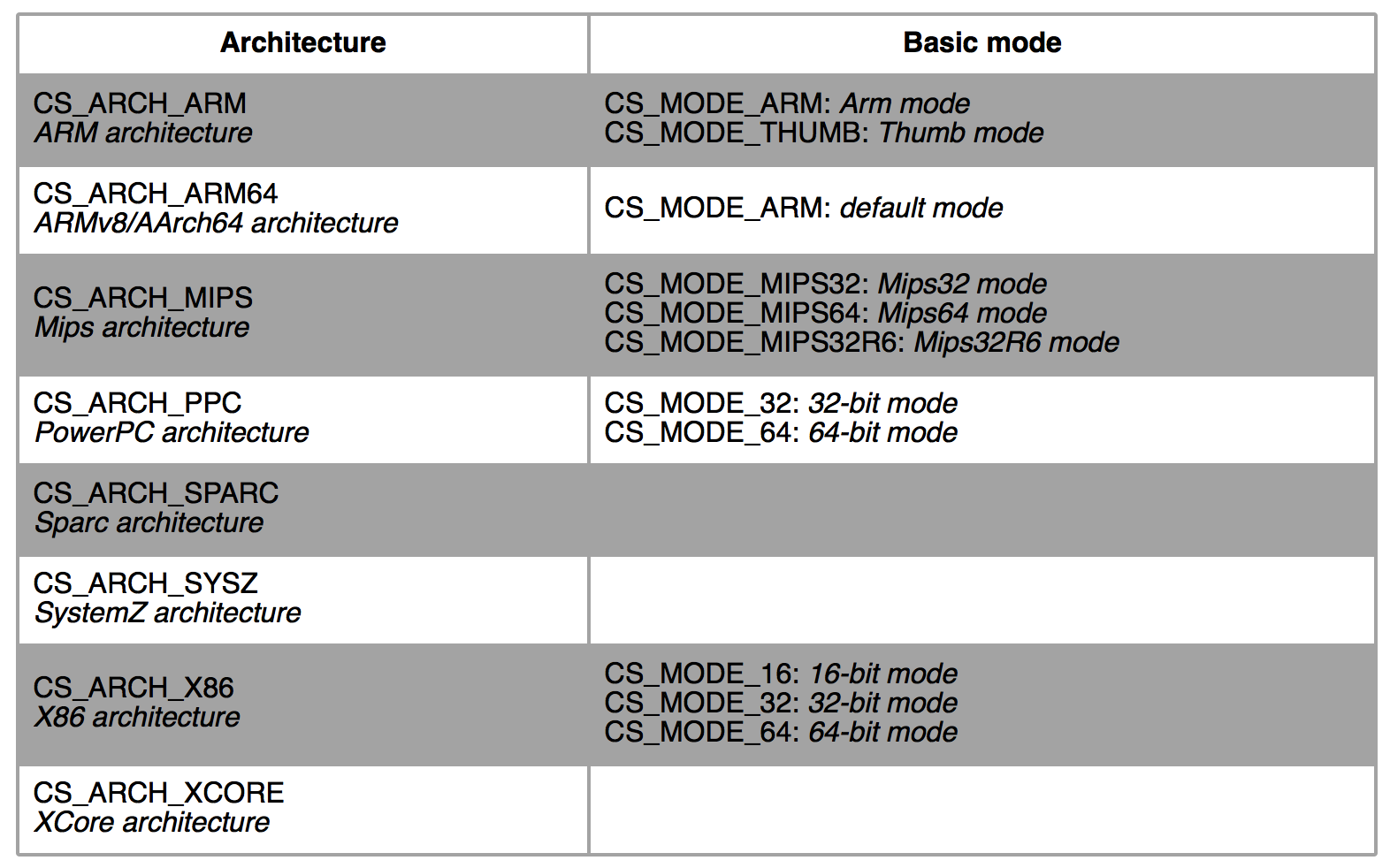
At the moment, Capstone supports 8 hardware architectures with corresponding hardware modes, as follows.
Besides, there are few modes to be combined with basic modes above.
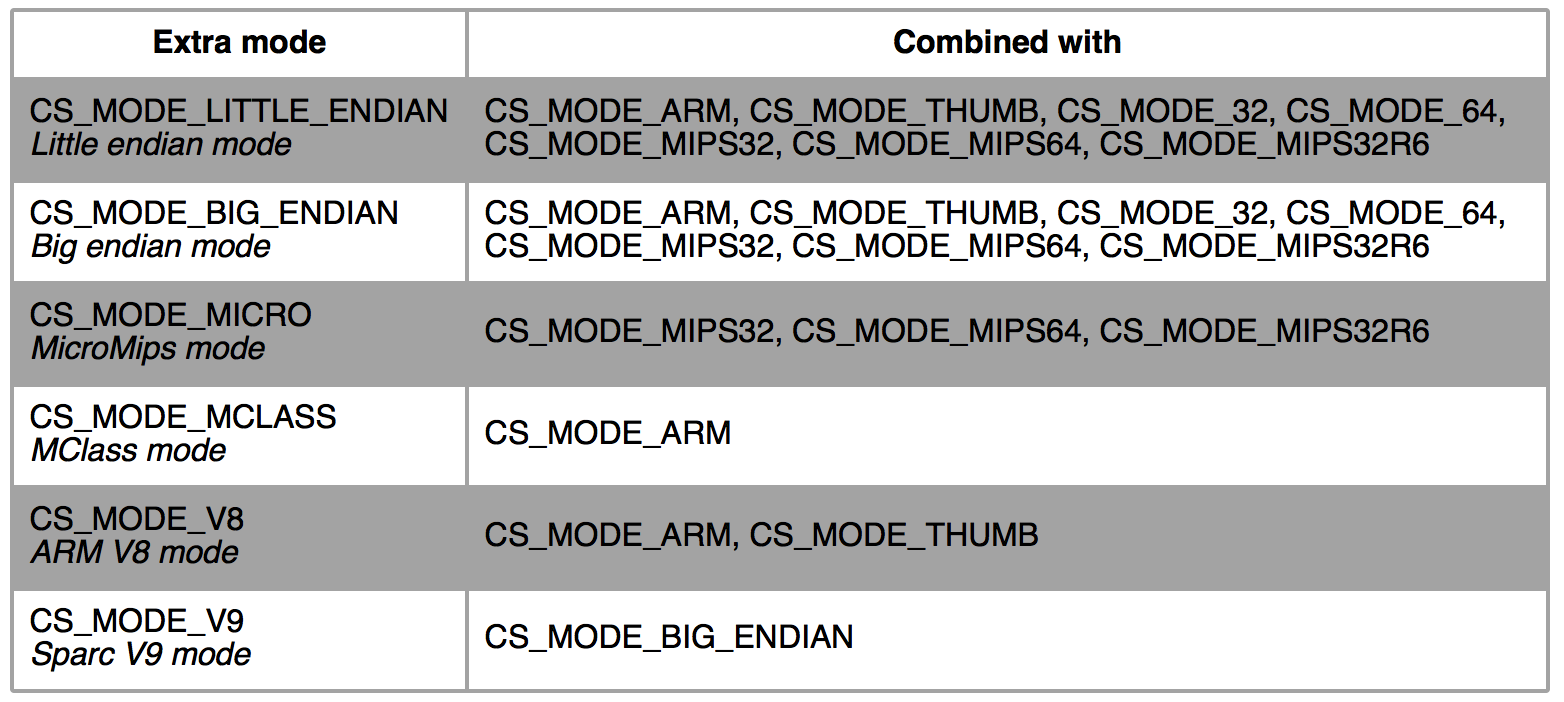
The way to combine extra modes with basic modes is to use the operand +. For example, the excerpt below initializes Capstone for Mips64 in little endian mode.
Capstone cs = new Capstone(Capstone.CS_ARCH_MIPS, Capstone.CS_MODE_64+Capstone.CS_MODE_LITTLE_ENDIAN);3. Set options
Capstone lets we customize the engine at run-time, so we can set the assembly syntax or turn on detail information.
3.1 Syntax option
By default, X86 assembly outputs in Intel syntax. To switch to AT&T syntax instead, we can simply set syntax option like below.
md = capstone.Capstone(Capstone.CS_ARCH_X86, Capstone.CS_MODE_32)
md.setSyntax(Capstone.CS_OPT_SYNTAX_ATT)
In case we want to return to Intel syntax, we can reset the syntax in the similar way:
md.setSyntax(Capstone.CS_OPT_SYNTAX_INTEL)3.2 Turn on details
By default, Capstone do not generate details for disassembled instruction. If we need information such as implicit registers read/written or semantic groups that this instruction belongs to, we need to explicitly turn this option on, like in the sample code below. However, keep in mind that this costs more memory, complicates the internal operations and slows down the engine a bit, so only do that if needed.
md.setDetail(true)
However, we can always reset the engine back to default state with similar method.
md.setDetail(false)4. More examples
This tutorial does not explain all the API of Capstone yet. Please find more advanced examples in source of Test*.java files under Java binding directory bindings/java in the Capstone source code.
